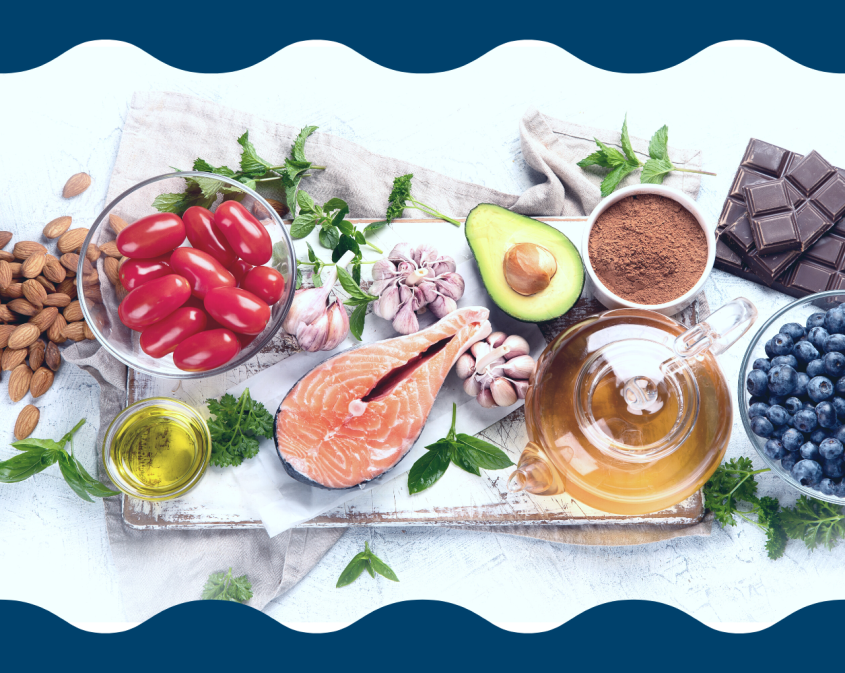

Anti-Inflammatory Diet Benefits
Inflammation is a necessary part of healing process. It helps the body fight illness and protect it from harm.
However, some people have a medical condition in which the immune system does not work as it should. This malfunction can lead to persistent or recurrent low-level inflammation that can be very harmful in the long run.
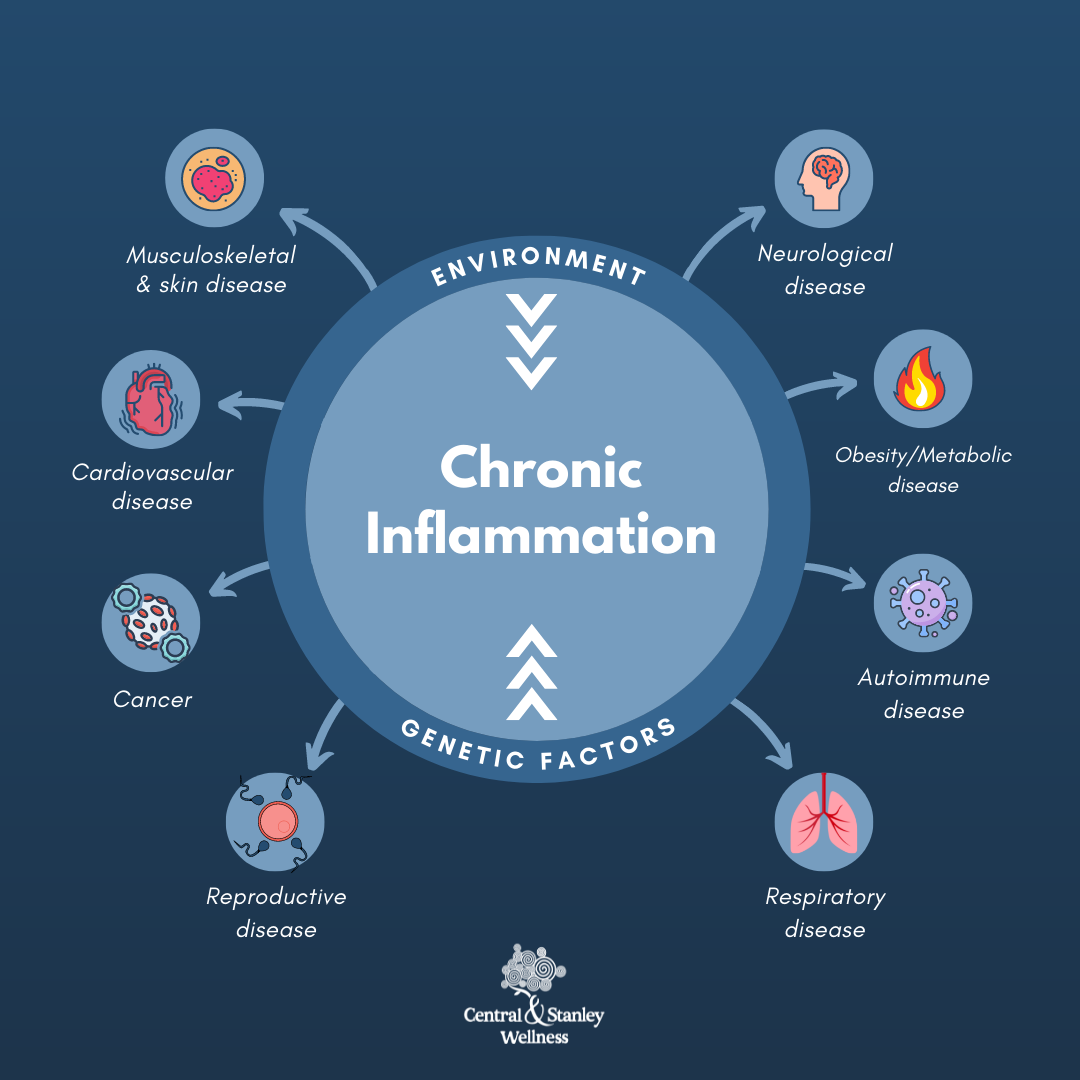
Chronic inflammation occurs with various diseases, such as psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and asthma. There is growing evidence that dietary choices may help manage the symptoms.
An anti-inflammatory diet favors fruits and vegetables, foods containing omega-3 fatty acids, whole grains, lean protein, healthful fats, and spices. It discourages or limits the consumption of processed & canned foods, red meats, and alcohol.
The anti-inflammatory diet is not a specific regimen but rather a style or pattern of eating.
What is an anti-inflammatory diet?
An anti-inflammatory diet focuses on fresh fruits and vegetables. Many plant-based foods are good sources of antioxidants. Some foods, can trigger the formation of free radicals. Examples include foods that people fry in repeatedly heated cooking oil. Some foods contain ingredients that can trigger or worsen inflammation. Sugary or processed foods may do this, while fresh, whole grain foods are less likely to have this effect.
Dietary antioxidants are molecules in food that help remove free radicals from the body. Free radicals are the natural byproducts of some bodily processes, including metabolism. However, external factors, such as stress and smoking, can increase the number of free radicals in the body. Free radicals can lead to cell damage. This damage increases the risk of inflammation and can contribute to a range of diseases.
The body creates some antioxidants that help it remove these toxic substances, but dietary antioxidants also help. An anti-inflammatory diet favors foods that are rich in antioxidants over those that increase the production of free radicals. Omega-3 fatty acids, which are present in oily fish, may help reduce the levels of inflammatory proteins in the body.
Who can it help?
An anti-inflammatory diet may serve as a complementary therapy for many conditions that become worse with chronic inflammation.
The following conditions involve inflammation:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Psoriasis
- Asthma
- Eosinophilic esophagitis
- Crohn’s disease
- Colitis
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Lupus
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
- Metabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome refers to a collection of conditions that tend to occur together, including type 2 diabetes, obesity, high blood pressure, and cardiovascular disease.
Scientists believe that inflammation plays a role in all of these. An anti-inflammatory diet may, therefore, help improve the health of a person with metabolic syndrome.
Eating a diet that is rich in antioxidants may also help reduce the risk of certain cancers.
Can a vegetarian diet reduce inflammation?
A vegetarian diet may be one option for people looking to reduce inflammation.
Anti-inflammatory diet tips
It can be challenging to transition to a new way of healthy eating & lifestyle, but the following tips may help:
- Pick up a variety of fruits, vegetables, and healthy snacks.
- Gradually replace fast food meals with healthy homemade food.
- Replace soda and other sugary beverages with mineral water and fresh cold pressed juices.
Other tips include:
- Talking to a Nutritionist or Healthcare professional about supplements, such as cod liver oil or a multivitamin.
- Incorporating 30 minutes of moderate exercise or Brisk Walk into the daily routine.
- Practicing good sleep hygiene (8 hours of sound sleep), as poor sleep can worsen inflammation.


